What is marketplace and how does it work?
The era of marketplaces, that began with the emergence of such popular platforms as eBay, Amazon and AliExpress, provided companies with new prospects of selling their goods to many customers. Let us discover what a marketplace is, how it works, what the difference between a marketplace platform and a simple online store, how people make money on marketplaces and what the necessary conditions for launching your own website of this type are.
Let us consider what it is and how it works:
➩Marketplace essence explained in simple words
➩How does a marketplace work: principles and rules
➩Differences between an online marketplace and an online store
➩How do marketplaces make money?
➩Pros and cons of a marketplace in terms of development
➩When is the best time to create your own marketplace?
➩Conclusion: how to develop your own marketplace solution
Marketplace essence explained in simple words
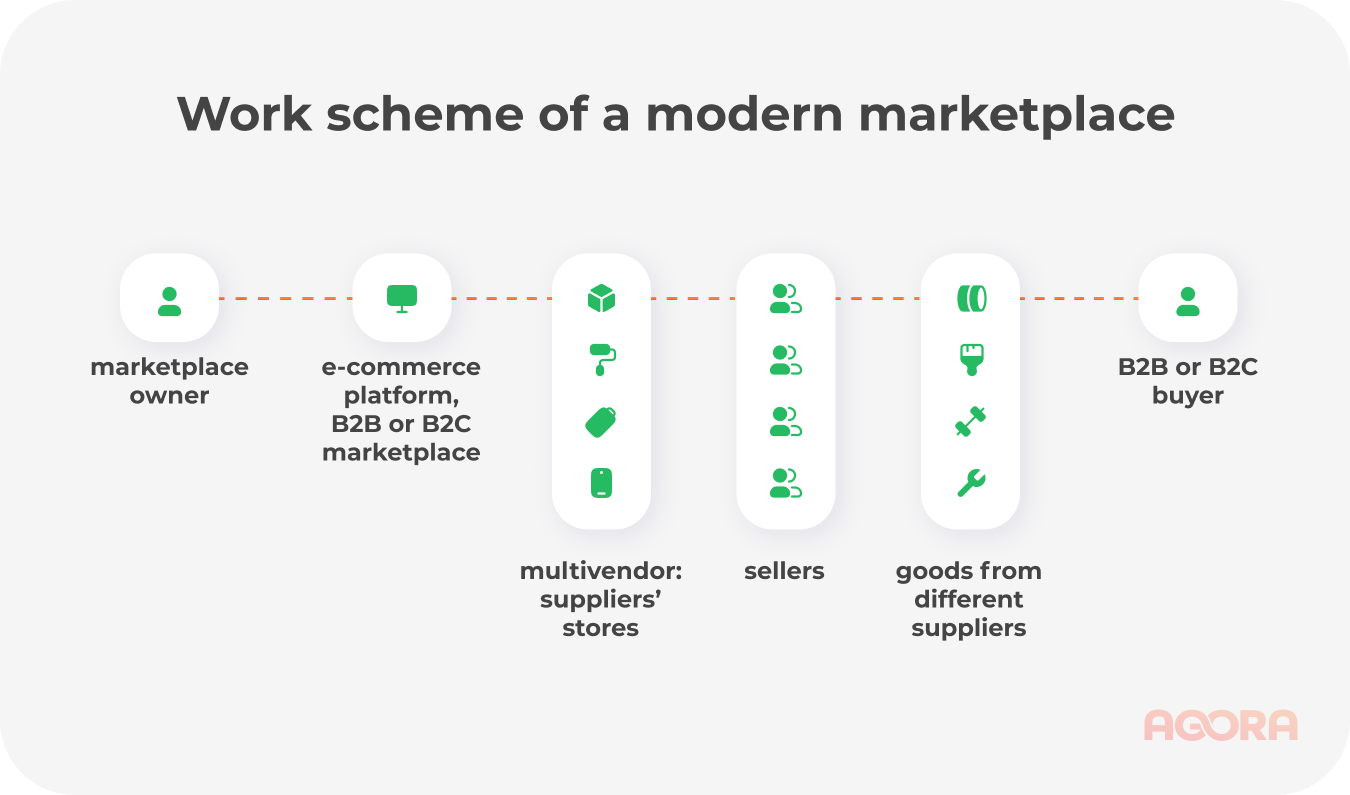
A marketplace is an e-commerce platform with many sellers offering their goods to multiple clients. Besides, not only goods can be sold on such a platform, but also services.

Contrary to general opinion that a marketplace is a purely multi-vendor website, on which thousands of suppliers work on equal terms, there are also niche solutions with one company acting as a seller.
The owner of the platform often doesn’t sell anything to the customers of the website, but offers services to sellers who open their stores. The owner earns money with commission on the goods sold, as well as other related services, such as credit or PRO subscription. However, there are also models according to which the platform sells the owner’s goods. These can be corporate platforms for large enterprises with the owner offering non-liquid assets and inventory items remaining.
The answer to the most popular question about marketplaces, which is “What is marketplace?”, is the following: it is something between a hypermarket and a shopping center, but it is Internet-based. It includes hundreds of departments, millions of goods and it can even offer individual boutiques and corners for particular sellers. Unlike a real store or mall, it is way easier to choose and compare different items, their prices and characteristics.
One of the areas gaining more attention in this segment is B2B marketplace where only legal entities, i.e. companies that act as sellers and buyers, can interact.
Main tasks of a marketplace
We have already seen the definition, now we will focus on its tasks. What functions does a marketplace platform fulfill?
- Rapid start of work with the launch of sales in the first days due to the MVP accelerated development. The basic version of the project has everything that you may need for a successful start. You can add necessary tools, options and modules later at any moment.
- Expansion of your target audience with affordable investments with quick return. Although a marketplace requires investments in user acquisition or increasing conversion, it does also provide the company with high profits by virtue of commission and additional payments.
- Simplification of logistics. Working through the network of distributors, dropshipping and selling directly from the warehouse of your supplier are easier to organize on a marketplace, as it offers a quicker and a more convenient delivery from the closest location to a client. It is also possible to rent the warehouses of logistics companies to quickly expand your presence.
- Geographical distribution. A business gets an opportunity to expand its presence and reach new regions and markets by entering such a platform.
- Digitalization of sales. Conducting all transactions through the platform, automating and optimizing business processes based on the best e-commerce practices. Billing and product matching, automatic uploading of product content from other systems, integrations with accounting software, automatic preparation of reports and analytics can be added in order to speed up work.
Examples of marketplaces
You can grasp how a marketplace functions by exploring the most popular platforms. The examples of these solutions, both in wholesale and retail segment, may be industry-specific or offer a wide range of goods to its customers. The best-known examples are the following:
- Aliexpress. A Chinese online-store that sells electronics, accessories, clothes, shoes and household items. The website works with sellers all over the world, while its audience is over 30 million buyers.
- Industry and niche marketplaces.
How does a marketplace work: principles and rules
Let us consider how it fulfills its functions, how its system works, and what the business logic of the project is. We will need several steps:
- Development and implementation of a marketplace, starting with an MVP, which takes from 2 to 3 months, with further scaling of the platform, introduction of integrations and additional options.
- Onboarding of suppliers: the registration of sellers on the platform. Verification is necessary in some cases. For instance, a marketplace for b2b.
- Loading a catalog or a store placed on the platform. In some solutions, for instance AGORAB2B solutions, this processes is optimized through the module of product matching and PIM system: you can easily add items using templates, as well as import or export the catalog in YML, XLS, etc.
- The creation of reference product cards accelerates the process of uploading and updating product cards on a marketplace. This is especially relevant when it is necessary to display offers of diverse suppliers in the product card on the platform. The work of creating cards would have required enormous amount of time, labor and money to pay for it, while reference product cards are templates already filled with data, from primary data base of the supplier’s or manufacturer’s product content, or automatically collected (parsing) from competitors’ websites. Such ready-made reference cards can be used by both content manager and supplier, it is only necessary to add your price to the reference card and monitor changes of the price list. Due to the product matching, the system can automatically gather databases of competitors’ cards with similar characteristics, and we will only need to create reference product cards. The products based on the AGORAB2B platform can include such modules if necessary. Advanced marketplaces have better systems of product matching with the option to automatically compare new products with the existing database of reference cards. For instance, it can be matching by category with automatic connection to the platform’s classifier with the distribution of goods into certain categories (for instance, repair goods, underwear, etc.). Besides, there is also background matching. It can continually analyze the database of previously created reference cards and compare them with suppliers’ price lists. As the basic data is being continuously updated, new goods can be integrated into the platform much faster. Apart from the main functions of auto-distribution, routing of items, filling new product cards according to the references, product matching allows you to automatically control the quality of the cards creation (data normalization). Given a high number of items that are received and updated on modern marketplaces, this option becomes a real “Holy Grail” for the owner of the platform. It helps maintain the quality of the marketplace content at a reasonable level while significantly saving the company’s money dedicated for this work.
- Placing goods in the warehouse of the marketplace or in your own warehouses in the regions of company’s presence.
- Selling goods to a client that found the right item on the website, studied its photo, description, compared it with its analogs and opted for the most suitable one. The marketplace’s owner should take care of the storefront and make sure that it is open for retail customers. If it is a wholesale b2b marketplace, then the owner should create a separate storefront with wholesale prices.
- Another important option is order routing. The routing service automatically distributes hundreds or even thousands of orders or business transactions within a matter of minutes. You can develop various scenarios, and the system will adapt to them analyzing every situation. For example, the system will consider if it is necessary to make customer’s data available to the supplier, or hide it; if it should allow the buyer to move the order to the next level or not (when an order is received, for instance), etc. Besides, during the order routing process artificial intelligence can make decisions which supplier of the marketplace will receive the order, depending on the price, cost of delivery and other set factors. When conducting procurement procedures, you can as well configure the routing of the order in different ways: for example, with a requisition document or by sending separate lines to the relevant buyers. You can create a variety of scenarios that the system will process automatically in one case or another. For instance, artificial intelligence will independently understand when to start the bidding procedure and when to proceed to the rebidding. All further steps will take place automatically at the platform level. You can modify the routing workflow if you take all sorts of parameters into consideration: what purchase costs or e-commerce order amount the system should take into account, what orders can automatically be transferred to the next status, which users should receive orders for approval, what roles and access levels they have, and what algorithm to apply if the required user is not available. In other words, routing is an particularly important function of modern marketplaces, and it can not only be easily configured depending on the tasks, but it can also learn due to its built-in artificial intelligence.
- Order payment, including with automatic payment splitting when the buyer’s payment amount is divided into the platform commission and the main part of payment for the supplier, which are sent to the corresponding accounts. Marketplaces can sometimes act as a guarantor of the transaction security (with the creation of a letter of credit). In this case, the amount paid for the goods is held as an escrow payment until the order is received by the buyer (the supplier receives the buyer’s money only after the terms of the transaction are fulfilled).
- Integration with logistics services and other systems via API.
- Confirmation of receipt and transfer of payment to the seller less the platform’s commission.
Differences between an online marketplace and an online stores
Before you start earning money on marketplaces, you should compare them to regular online stores in order to find out which model will be more profitable for your company. The following features are the most important to consider:
- Source of income. Income in online stores is limited to sales revenues, while marketplaces profits are the result of both selling your own goods or non-liquid assets and payments for commissions, subscriptions and additional services, such as providing sellers with a credit line or renting a warehouse.
- Brand development. If an online store is created for developing the brand of the owner company, marketplaces, even those developed for one owner, are focused on sales and act as an intermediary between sellers and buyers.
- Stock. Online stores sell products of one or more brands, while marketplaces offer a variety of similar items from different manufacturers. Therefore, the stock of marketplaces can be vastly superior to the number of products of a single store.
- Items in demand. Marketplaces are always better at selling seasonal items or products at the lowest price. At the same time, the most popular items of online stores may be different. That is why you should take into account the demand for the solution and its relevance to the market when creating and developing your marketplace.
- Content filling and moderating. Marketplaces have a more complex content management system. Content filling and moderation of product cards and other information in an online store occurs through the marketing department, and as soon as agreed, they are later placed on the storefront by the content manager. On marketplaces, suppliers upload content to their stores independently. The owner of the platform therefore needs to monitor thousands or even tens of thousands of items daily, which can’t be done manually. Consequently, any marketplace needs automation mechanisms: product matching, checking for stop words or filtering junk content, deleting outdated and non-unique information.
- Offline store. An online store is often linked to a real store, while marketplaces don’t have offline stores, although they often deliver goods through pickup points.
- Internet audience and traffic. Compared to online stores, marketplaces spend disproportionately large resources on attracting traffic, so they are always at the top of search results and can boast a much wider audience. At the same time, getting into the top of search engine results requires a lot of investment from marketplaces, and the approach to the target audience varies a lot. The key goal is to achieve a constant return of the client to the platform, while the goal of an online store is to earn from every order since it has a large margin from each one.
- Geography of presence. Large marketplaces have an adjusted process for entering the markets of other regions and countries, including multilingual and multicurrency options, as well as the opportunity of placing new warehouses, while it can be quite difficult for online stores to go beyond their original country. There are also nuances from the point of view of logistics. For example, almost all B2C marketplaces work with pickup points and have their own logistics, while a marketplace for b2b usually delivers its goods through suppliers.
- Maintenance costs. For the marketplace owner, the costs of its support and promotion are paid off by income from commissions, sales of related services and goods of his or her own brand. In exchange for a commission, suppliers receive service, maintenance and the opportunity to offer their products to a wide audience of potential buyers. In such a win-win strategy, all marketplace participants win. Maintaining an online store requires a lot of time and effort, and the owner receives return due to the profit from sales after a longer period of time.
- Launch and work starting periods. A regular store can be launched in a week. Even though a marketplace is a complex project, it can be created based on the ready-made AGORAB2B platform within the period of two to three months and implemented in a week. Entering a marketplace implemented by AGORAB2B will take only one day, or even a few hours, due to the catalog export with the PIM module.
How do marketplaces make money?
Let us consider the sources of income of a marketplace solution. How can the owner of the platform earn an income?
- Sales commission. This is the most common option: the platform keeps a fixed percentage from each transaction. There are also other types of commission for additional services, such as storage of goods in the warehouse of the marketplace, pre-sale package, return in case of refusal.
- Premium access. It is also a way to make money on marketplaces focused on buyers. Such a payment is a subscription that offers additional bonuses to customers: free shipping, or increased discount.
- Payments for placing goods in the catalog. It is a commission for sellers that implies that a new item can be placed in the catalog and sold only with an additional payment.
- Subscription. It is a payment to access advanced functionality that can be offered to both sellers and buyers. For instance, it can be a self-learning search, the opportunity to search goods by item numbers and characteristics of items, or the option to compare several analogs.
- Promotion to the top. A commission for promoting particular items or an entire store of a seller to the top of the site is another popular way to make money on marketplaces.
- Payments for additional services. The platform may offer other special options, such as suppliers crediting or goods insurance, and marketplaces act as an independent escrow agent that guarantees the transaction security.
Types of marketplaces
What types of trading platforms exist, depending on the type of interaction between trade participants, the subject matter of the proposal, and the features of the product stock?
The following types are distinguished according to the type of interaction participants:
- B2B: a business conducting wholesale trade with another business;
- B2C: a business offering goods and services to at retail to end customers, individuals;
- C2C: individuals working with other individuals;
- B2B/B2C: a mixed type; a business working with another business to sell goods to retail customers;
- D2C: a manufacturer directly selling its goods to retail customers;
- G2B: a state selling goods to a business.
According to the proposals, the following types can be mentioned:
- Goods.
- Services.
- Information aggregation.
- Investment.
- Banks.
The types according to the features of the stock:
- Selling goods from one manufacturer or working in the same segment with different brands: for example, a marketplace for selling Michelin tires developed by AGORAB2B.
- SRM corporate marketplace developed for small purchases of one company.
- Marketplaces of goods with common specificity.
- Platforms for selling non-liquid assets, such as raw materials and inventory items of large industrial enterprises.
- Complex large global platforms offering goods of all categories, working both within the country and around the world, such as AliExpress.

Pros and Cons of a marketplace in terms of development
Creating and launching your own marketplace has both advantages and disadvantages. Here are some reasons why buyers of such solutions look for their own way to start making money on trading platforms:
- Quick development which takes from 2-3 months and the launching process of one week. When creating a project based on the AGORAB2B b2b platform, there is no need to develop your own website from scratch. An experienced team will tell you what to pay your attention to in the beginning, and the customer will have the opportunity to carefully study the market and test promising models during platform creation.
- Minimal expenses to get started: there is no need to hire a lot of staff and a development team, as well as to invest in long and expensive customized development.
- You will set your own rules, collect your own database of trusted suppliers, and achieve the best prices and terms of cooperation.
- Independent determination of the commission size and additional payments which can be of 4-5%, or 20-25%.
- Quick connection of the necessary functions, additional options, integrations with adjustment to the market needs.
- Automation of the processes of collecting statistics and preparing analytics, tools for stimulating demand and increasing sales.
We can note one more indisputable advantage for modern companies that seek scaling and increasing investments. Implementing your own marketplace will always have a positive impact on your company’s capitalization, as well as related business benefits. For example, when creating an IPO. If you have your own online store, a marketplace will allow you to discover additional potential for optimizing the business model of the company’s e-commerce. Besides, according to experts, a company’s own marketplace is always more valued than an online store.
However, you also have to take into account the problems that may arise during development:
- A marketplace is a complex solution requiring attention to the stability and security of the system, its ability to withstand high loads and maintain the integrations with third-party solutions stability.
- The development of such a project is an expensive and time-consuming process requiring involvement of the top management of the company.
- Advertisement costs are a necessary component of promoting a business and bringing the website to the top of search results. This may require constant investment and increased focus on SEO, preparing quality content, attracting traffic, increasing conversions.
- It is necessary to maintain a balance between the number of sellers and buyers on the platform, offering favorable terms of cooperation to both.
- The need to organize turnkey sales with the seller being responsible for bringing goods to the warehouse, and the marketplace being responsible for storage, sale and delivery to the client. The platform owner may need to rent a lot of warehouses, think logistics through, cooperate with logistics service providers.
Development features
Having understood what a marketplace is and how to make money on it, you can make a decision whether to launch your own solution of this type to sell your products or attract third-party vendors. Let us also see what difficulties companies face when creating a marketplace platform:
- Product incompatibility with market demands. Even complex solutions like marketplaces require studying the needs of audience, testing business hypotheses, and preliminary experiments with landing pages and business options so as to be sure of the product-market fit.
- The need for significant investments when launching a large project. A platform of AliExpress scale can’t be implemented with a small budget without investing in the logic and business processes development, as well as user behavior scenarios on the website.
- Non-specific and not business-related objectives. Even with a relatively large budget, it makes no sense to implement an idea that has little effect on development of the company and doesn’t contribute to increasing sales.
- Aspiration to connect the maximum functionality in the very beginning. There is no need to implement everything at once: most companies eventually realize that a part of the implemented functions was not used.
- Requirement to strictly follow the terms of reference. The reason here is the same: in the process of development and implementation of the marketplace, a lot will change. It is more important to quickly respond to market changes than to carefully adhere to the original plan.
When is the best time to create your own marketplace?
It makes sense to think about creating your own marketplace when access to existing website becomes unprofitable. It can’t lead a company to success if:
- The selected segment or product category is a narrow niche solution that won’t be in demand by a large number of buyers and risks being lost among the other consumption goods.
- Selected products belong to the category of perishable goods and cannot be stored in a warehouse for a long time.
- Your product is from the luxury or premium category. At this stage, many buyers of multi-category marketplaces prefer cheaper products, so separate solutions are needed in order to sell goods in the luxury segment.
- You work with specialized products, such as industrial products: railway rails, sleepers, materials of the upper construction of the roads, and other specific products that cannot be sold on regular marketplaces.
Conclusion: how to develop your own marketplace solution
Although a marketplace is a complex project, during the development of which you must consider many factors, you can significantly reduce the time and costs of creating your own B2B, B2C or C2C platform with the AGORAB2B platform, available on SsaS or On-Premise terms.
The development of a marketplace takes place according to the constructor principle by linking the desired modules with the use of low-code. There are more than 200 modules to choose from. It enables you to quickly change the business model of the project by testing various hypotheses. The development of an MVP takes at least two months, and you will be able to implement the project in a week.
The AGORAB2B e-commerce platform withstands high loads and is adapted to the requirements of complex e-commerce projects. It offers:
- management of many user roles with access restrictions depending on the competence of every specialist;
- multi-level pricing and discount patterns;
- the ability to design the interface according to the corporate brand book;
- wide content personalization, including prices, discounts, stock and accounting units of goods in the catalog, payment and delivery features;
- integration with business systems, such as ERP, CRM, SRM, EDI with the use of CPU;
- logistics calculator and billing system connection;
- product matching, self-learning search, export manager for quickly adding product content;
- automated collection of statistics, preparation and uploading of analytical reports;
- built-in marketing tools.
The AGORAB2B team will provide the full range of development and implementation services of the project, offer staff onboarding, further technical support, timely updating and modification of the complex website system according to the marketplace model.
Also read


